In the third part of our complete forex trading course for beginners, I'm going to show you how to use indicators to better analyze trends and be able to predict price movement
If you haven't read the previous parts of this Forex Guide for Beginners, I strongly recommend you to do so before reading the current section. Here are:
- Forex Trading Course for Beginners - Forex Fundamentals [Part 1/4]
- Forex Trading Course for Beginners - Forex Charts & Trends [Part 2/4]
Now that you did it and know the FOREX fundaments and how to correctly read the charts let's move into indicators.
9. An Overview of Forex Indicators
An indicator is a tool that helps you analyze price movements. There are two groups which most indicators fall into –trend-following indicators are the most useful when the price is trending in one direction or the other, meanwhile oscillating indicators can be helpful when the price is consolidating into a range. It is important to know which group the indicator you are using falls into and to choose the correct indicator for each situation.
Below we cover some of the most popular indicators used by currency traders.
9.1 The Average Directional Index (ADX)
ADX The Average Directional Index is a special type of trend follower that can also help you decide whether a trend follower is, in fact, the best tool for the job at that particular moment. Trend-following indicators will function best when the ADX is over 30. When it is below 30, then an oscillating indicator may be a better choice.
When the ADX is rising, this indicates that the trend is gaining in strength, and when it begins declining it is a sign that the trend is losing steam and a trading range may soon develop. Likewise, when ADX begins rising again it indicates that price is breaking out of its range and a new trend may emerge. The ADX does not however show which direction the trend is going (up or down), only its strength.
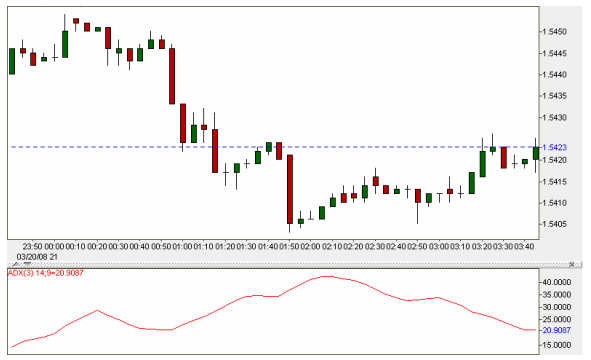
In the example above, note how the ADX starts off low as the price is trading within a range near the left side of the chart. Then, as the price begins dropping, the ADX rises above 30 to indicate a trend is in progress. The ADX also confirms that the trend is over by beginning to decline once again. And when it finally drops below 30 we find ourselves trading once again in a tight range.
Check below a video tutorial that explains in detail what the ADX indicator is and how you can use it:
9.2 MACD
MACD or the Moving Average Convergence Divergence measures the difference between a short-term and longer-term moving average. When the red line crosses above the blue line it indicates an uptrend, and when the red crosses below the blue it indicates a downtrend.
Additionally, the green bars (called the MACD histogram) give us an indication of the trend’s strength or weakness. And, unlike the ADX, they also show us the overall direction of the trend. Longer bars indicate increasing strength, and shorter bars indicate decreasing strength.
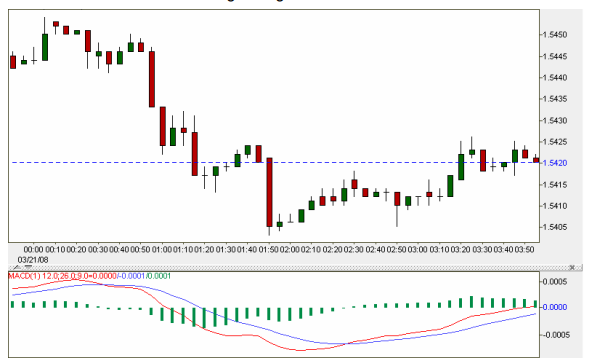
In the above example, we see the red MACD line fall below the blue one as price begins its move downward. The green bars in the histogram are increasing in length as well, indicating that the down-trend is gaining momentum. When the price reverses momentarily to head up, the histogram reflects a loss of downward strength. Downward strength resumes as the next long red candle posts on the chart.
However, it is important to note that while the price made a lower low, the histogram did not make it quite as far down. This is known as a bullish divergence and indicates that the trend will soon end and be followed by a reversal.
Here is a good video tutorial that explains exactly how to use the MACD indicator, as well as goes over an effective MACD trading strategy.
9.3 Momentum
The momentum indicator measures the rate of change in closing prices, and functions very similarly to the MACD histogram. It is often useful in identifying likely reversal points due to its ability to detect trend weakness.
In the example below, the moment indicator perfectly identifies the point at which the downtrend ends and the new uptrend emerges. As we near the end of the downtrend, the momentum indicator begins tracing a bullish divergence. When momentum is below zero and turns sharply upwards following a bullish divergence, it can signal a long entry.
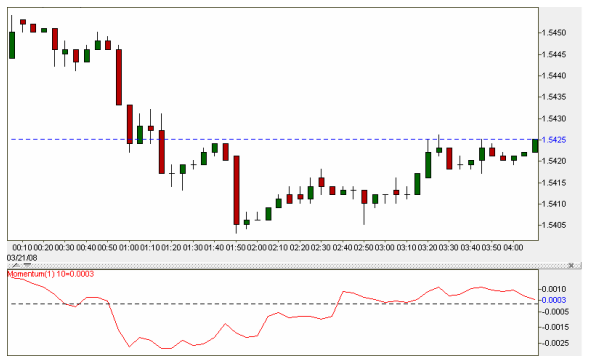
Similarly, when it is above zero and turns sharply downwards following a bearish divergence, it can indicate a potential short entry. As we near the right edge of the chart, we see that momentum is indicating that the uptrend is nearing an end and a reversal may be imminent.
In the following video tutorial, you will find out why the Momentum Indicator represents one of the best forex indicators for scalping (scalping Forex tips) and how to identify and follow the trend using Momentum indicator and what are the best settings for the indicator (day trading momentum trading strategy).
9.4 Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are volatility bands placed x standard deviations around a moving average. Developed by John Bollinger, the bands widen in periods of increased volatility and narrow when volatility decreases.
Traditionally, the bands are used to highlight potential oversold and overbought areas. For example, if a price move breaks the upper band, then the price can be expected to return to its mean, or in this case, the mean moving average.
Calculation:
- Middle Moving Average = 20-period simple moving average (20 SMA).
- Upper Band = 20 SMA plus the 20-period standard deviation multiplied by 2.
- Lower Band = 20 SMA minus the 20-period standard deviation multiplied by 2.
9.5 Stochastics
Stochastics consist of a fast line and a slow line, and oscillate between 0 and 100. Levels above 80 are said to be over-bought and levels below 20 are referred to as over-sold. When the red line crosses above the blue we know that the bulls are overpowering the bears. When the red line crosses below the blue, on the other hand, we know that the bears are beginning to overpower the bulls.
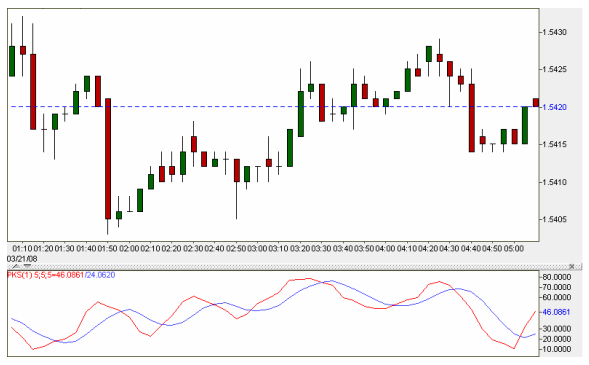
It is best to enter long positions when stochastics first cross above 20, returning from over-sold conditions. This indicates the greatest amount of “room” left for an upward move. As stochastics near 80, we know that we are closer to the end of the move rather than the beginning of it, and may consider staying out of the trade if not already in it from before.
As the stochastics begin to turn and cross, we are given a signal to close any remaining long positions. As they cross back below 80 and return from overbought conditions, we may look to enter short. If the stochastics are closer to 20 than to 80, we may wish to think twice about entering into any new short positions.
Once they cross, we would also look to close any short positions already open from before. Then, as the stochastics break above 20, the cycle repeats and we begin looking to enter long once again.
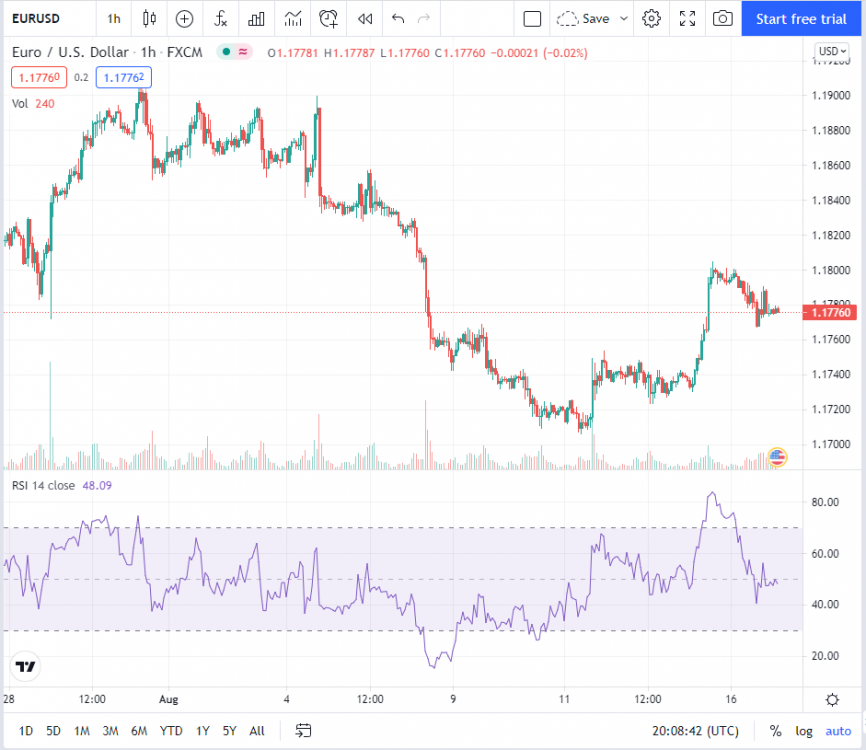
9.6 Relative Strength Index (RSI)
Developed by J. Welles Wilder the Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum oscillator that measures price movements' direction and velocity.
The Relative Strength Index is similar in its function to stochastics, except it uses 30 to indicate oversold conditions and 70 to indicate over-bought. RSI signals a potential long when it breaks above 30, and a potential short if it comes from above and breaks below 70. In addition, levels above 50 confirm an uptrend, while levels below 50 indicate a downtrend.
The indicator compares upward price movements in the closing price to downward movements in the closing price over specific time periods. The default period, suggested by Wilder, is 14 periods.
Calculation:
RSI = 100 – 100 / (1 + RS)
Where RS equals Average Gain divided by Average Loss
- Average Gain = [(Sum of gains over previous 14 periods / 14) * 13 + current gain] / 14
- Average Loss = [(Sum of losses over previous 14 periods / 14) * 13 + current loss] / 14
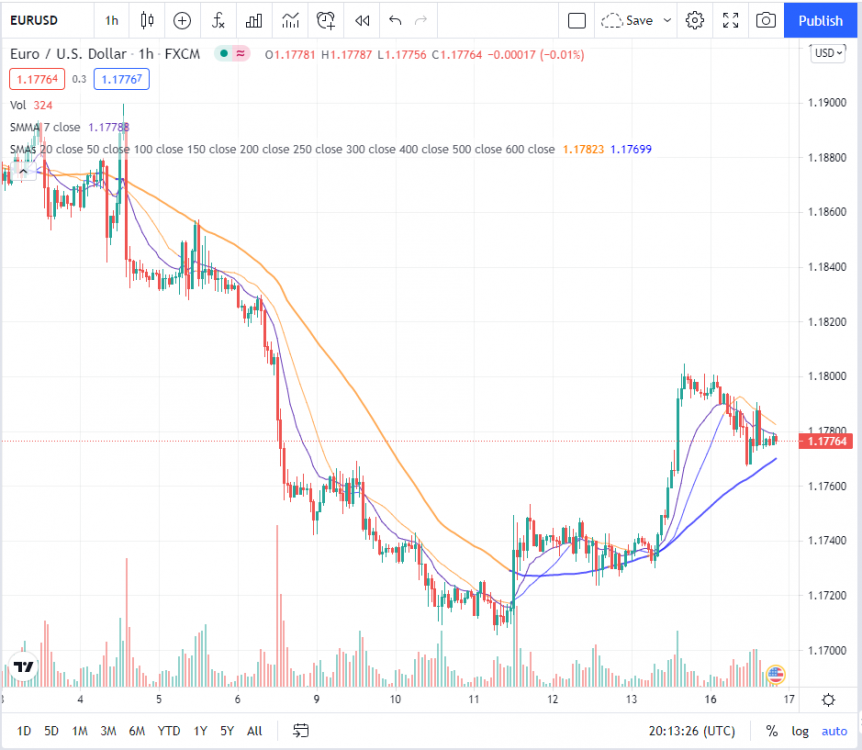
9.7 Simple Moving Average Line
SMA or simple moving average is the most common indicator plotted on forex charts.
Moving averages are used to help smooth price fluctuations over a certain period, giving the trader a clearer picture of the direction of the price movement.
Calculation:
SMA = Sum of the closing prices/number of periods.
10. Top 3 Forex Trading Strategies
10.1 Support & Resistance
Preferable timeframe: 1h
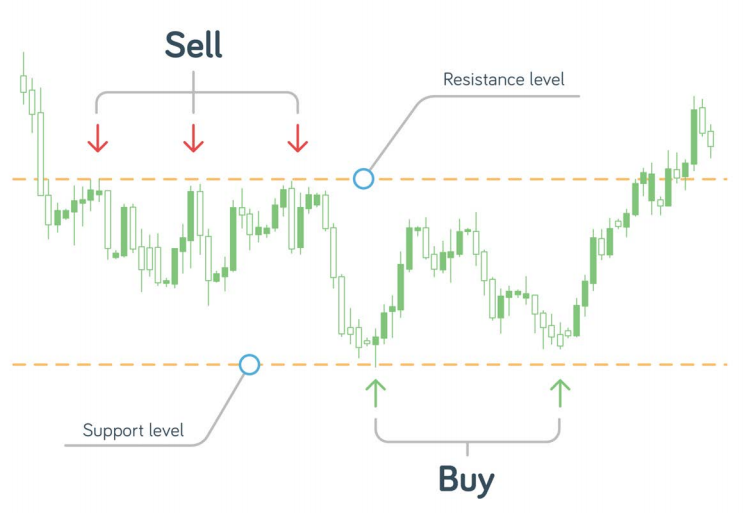
This strategy follows the old business cliché, “buy low and sell high.” Forex traders quantify how low a price’s low and how high it is by analyzing areas where prices have stopped and changed direction.
The support refers to the level where the price rarely falls below before turning around, and the number of buyers exceeds that of sellers hence causing the price to rise.
On the other hand, the resistance is the level where price rarely exceeds, and the number of sellers exceeds that of buys hence lowering the price. In both cases, the price stops and turns around.
Check our article on how to trade using support and resistance zones.
10.2 Pinocchio Strategy
Preferable timeframe: 1h, 4h
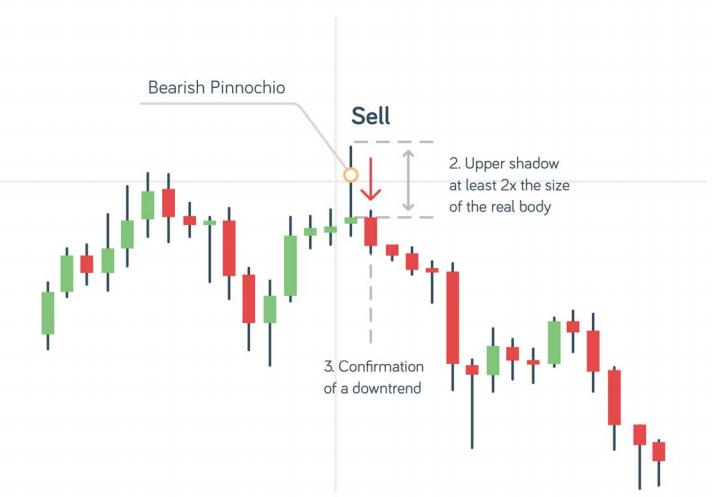
A Pinocchio bar is a candlestick bar with a tiny body and a very long wick (nose). It is also called Shooting Star, Hanging Man, and Gammer. You may remember that Pinnochio's nose grew long when he was lying.
The same happens with this strategy: when the wick is longer than the body, this tells us that the market is deceiving us and that we should trade the opposite way.
The entry point varies: some traders prefer to wait for the next candle to retrace to the 50% Fibonacci level of the Pin bar, while others enter immediately after the Pin bar closes. A long wich indicated strong selling pressure; a long tail suggests intense buying power.
10.3 The Double Red Strategy
Preferable timeframe: 5min
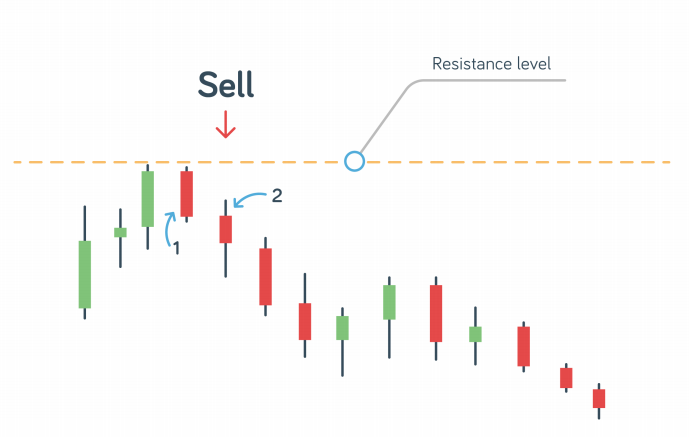
The double-red strategy is a short-term reversal system based on price action and resistance. The trade is planned on a 5-minute chart and signaled when two bearish candles follow a resistance test.
How to make a profit?
Choose an asset and watch the market until you see the first red bar. Then wait for a second red bar. If the second red bar closes lower than the first red bar, then it's a jackpot. Usually, what happens is that the third bar will go even lower than the second bar. This is the point where you should open a short position.
Quick recap
In the third part of our FOREX guide you learned what are ones of the most used FOREX indicators (ADX, MACD, Momentum, Bollinger Bands, Stochastics, RSI, SMA) and three Forex trading strategies you can use to make a profit on trading currencies.
In the last part of the guide you will learn about psychology of trading, systems you can use and what brokers you should choose.









.thumb.jpeg.89a9ef7623f450c9051242cc525fb1c5.jpeg)






